A
ABM :
Account-Based Marketing (ABM) is a strategic approach that focuses on a select group of high-value accounts rather than a broad target audience. It’s a personalized, one-to-one marketing strategy designed to build strong relationships and drive conversions.
AIDA :
Attention/Awareness, Interest, Desire, Action.
The four steps of the old Purchase Funnel, wherein customers travel from consideration to purchase. See also current purchase
A/B Testing :
Also known as Split Testing. Comparing two versions of a digital element (ad, landing page) to see which performs better. [Jump to Conversion Rate Optimization (CRO)]
Attribution Modelling :
Identifying which marketing touchpoints influenced a customer’s purchase decision.
B
Backlink :
A link on another website that points to your website. Important for SEO. [Jump to Search Engine Optimization (SEO)]
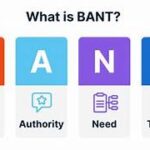
BANT :
Budget, Authority, Need, Timeline. Link to article.
B2B (Business-to-Business) :
Marketing directed at other businesses.
B2C (Business-to-Consumer) :
Marketing directed at individual consumers.
Black Hat SEO :
Unethical SEO practices that can get your website penalized by search engines. [Jump to Search Engine Optimization (SEO)]
Blog :
A website with informal, regularly updated content.
Bounce Rate :
The percentage of visitors who leave a website after viewing only one page.
Brand PPC :
Brand bidding, also known as PPC brand bidding, is the practice of bidding on branded terms or branded keywords belonging to your company. This way, your ads appear when your brand name is entered as a search term. The goal is to direct traffic to your site in the “above the fold” paid search results area and help prevent competitor’s hijacking your brand terms.
Brand Storytelling :
This marketing strategy uses storytelling techniques to connect with consumers on an emotional level. Effective brand stories can build a strong emotional connection with your target audience, leading to long-term brand loyalty.
C
Call to Action (CTA) :
A clear instruction telling users what to do next, such as “Buy Now” or “Sign Up.”
Cannibalization (Keyword Cannibalization):
When multiple pages on your website compete for the same keyword ranking in search engines. [Jump to Search Engine Optimization (SEO)]
Chief Marketing Officer (CMO):
The most coveted job in the marketing organization chart. A CMO’s skill set is rooted in marketing fundamentals but expands into personnel development, quantitative analysis, and strategic thinking.
Click-Through Rate (CTR) :
The percentage of people who click on a link after seeing it.
Cloud Computing :
Storing and accessing data and programs over the internet instead of on a local computer.
Content Delivery Network (CDN) :
A global network of servers designed to deliver your website’s content faster, more reliably, and more securely to users—no matter where they are in the world.
Content Management System (CMS) :
A software application that allows users to create, edit, and publish content on a website.
Conversion Rate :
The percentage of visitors who take a desired action on your website, such as making a purchase. [Jump to Conversion Rate Optimization (CRO)]
Conversion Rate Optimization (CRO) :
Techniques for improving the percentage of visitors who take a desired action on your website. CRO marketing is a method of increasing the percentage of your website’s visitors who take a desired action (or, to use marketing speak, who ‘convert’). Conversions are a marketer’s holy grail, but the term can mean different things depending on your company’s goals
Cost Per Click (CPC) :
An advertising pricing model where you pay each time someone clicks on your ad.
Cost Per Mille (CPM) :
An advertising pricing model where you pay for every 1,000 impressions (views) of your ad.
CPA (Cost Per Acquisition):
The cost of acquiring a new customer.
CPL (Cost Per Lead) :
The cost of acquiring a new sales lead.
CRM (Customer Relationship Management) :
A software system that helps businesses manage their interactions with customers.
CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) :
A language that controls the style and layout of a website.
CTQ (Critical To Quality) :
CTQs are the internal critical quality parameters that relate to the wants and needs of the customer. The (internal and external) customer requirements get translated into Critical-To-Quality (CTQ) features. These CTQs define the criteria to evaluate what good looks like i.e., how well the project scope and deliverables meet requirements. CTQ is a simple, yet powerful tool that translates customer needs into a Meaningful, Measurable, and Actionable metrics for people or group of people.
CTR (Click-Through Rate) :
The percentage of people who click on a link after seeing it. [Already defined above]
D
Data Analytics :
The collection, analysis, and interpretation of data to improve marketing strategies.
Data Architecture :
Imagine a city! Data architecture is the blueprint for how data is organized (like streets and neighbourhoods), stored (buildings), and used (traffic flow). It includes things like data models (maps), schemas (building codes), and data flow diagrams (traffic patterns).
Data Breach :
This is like a break-in! It happens when unauthorized individuals access confidential information, such as customer records or financial data. Yikes!
Data Broker :
Think of them as data middlemen. Data brokers collect massive amounts of user data (browsing history, interests) and sell it to advertisers and publishers. Ideally, this helps make online ads more relevant to you.
Data Controller :
The “boss” of the data! They decide why and how personal data is used. Think of them as the CEO who sets the goals for handling customer information.
Data Infrastructure :
This is the foundation on which your data operations rest. It includes the hardware, software, and processes that keep your data flowing smoothly. Like the pipes and cables that power a city!
Data Lake:
Imagine a giant reservoir! A data lake stores raw data from various sources (rivers) in its original format (untreated water) until it’s needed for analysis (purification).
Data Layer :
This is like a hidden message! It’s a layer of code on a web page that secretly communicates information between the page and the tag management system, helping track user behaviour.
Data Management Platform (DMP) :
Advertisers use DMPs like a “super address book.” They upload customer data and audience information to create more targeted advertising campaigns.
Data Minimization :
This principle is all about “less is more.” It means collecting only the essential data needed for a specific purpose, not stockpiling everything.
Data Processor :
This is the “data worker.” They only process data on behalf of the controller, following their instructions. Think of them as the team that manages the data according to the CEO’s plan.
Data Protection:
It’s like putting a security fence around your data! Data protection is all about safeguarding personal information and ensuring it’s handled responsibly.
Data Security:
This is the “data bodyguard.” Data security protects digital information throughout its lifecycle, preventing corruption, theft, or unauthorized access. Think of it as keeping the data safe from intruders.
Data Subject:
You are the data subject! It refers to any individual whose personal information is being processed by an organization.
Data Subject Access Request (DSAR):
This is your right to know! You can submit a DSAR to an organization to access and understand how your personal data is being used.
Data Warehouse :
Think of it as a giant library for your data! A data warehouse stores information from various sources in a structured format, ready for analysis.
Database:
This is a more focused storage unit. Databases hold structured data for a specific purpose, like a company’s financial records stored in a finance database.
Demand-side Platform (DSP):
This is an advertiser’s “bidding tool.” Advertisers use DSPs to automatically participate in ad auctions and exchanges, helping them place their ads in front of the right audience.
Demand-side Platform (DSP):
This is an advertiser’s “bidding tool.” Advertisers use DSPs to automatically participate in ad auctions and exchanges, helping them place their ads in front of the right audience.
Denormalise :
Imagine copying information in a library for faster access. Denormalization intentionally repeats data across tables in a data warehouse to optimize it for quick reading and analysis.
Digital Asset Management (DAM) :
Storing, organizing, and accessing digital files.
Display Advertising :
Online advertising that appears in banner, image, or video format.
Domain Name :
The unique address that identifies a website on the internet.
Descriptive Schema :
This is like designing a website with your own needs in mind. A descriptive schema structures data to suit your company’s internal needs, rather than necessarily catering to marketing vendors.
Developer Tools :
These are like the toolbox for a web mechanic! Your browser provides a set of tools to debug and troubleshoot various aspects of a website, essential for technical marketers.
DNS (Domain Name System) :
Think of it as the internet’s phonebook! The DNS translates human-readable domain names (like teamsimmer.com) into numerical IP addresses that computers understand.
E
Ecommerce :
The buying and selling of goods and services over the internet.
Email Marketing :
Sending commercial messages to a group of people using email.
Engagement :
The level of interaction between a brand and its audience.
F
Facebook Ads :
Paid advertising on the Facebook social media platform.
G
GA (Google Analytics) :
A free web analytics service offered by Google.
Growth Hacking :
Rapid experimentation to find effective ways to grow a business.
H
Hashtag :
A word or phrase preceded by a hash symbol (#) used to categorize content on social media.
Heatmap:
A visual representation of how users interact with a website.
I
Inbound Marketing :
Attracting customers by creating valuable content and experiences.
Influencer Marketing :
Partnering with influential people to promote your brand.
Interstitial Ad:
An ad that appears between content on a website.
J
JavaScript (JS) :
A programming language used to create interactive web elements.
JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) :
A lightweight format for storing and transmitting data.
K
Keyword :
A word or phrase that people search for on the internet.
L
Landing Page :
A web page designed to capture leads or conversions. [Jump to Conversion Rate Optimization (CRO)]
Lifecycle Marketing :
Marketing messages tailored to different stages of the customer journey.
Link Building :
The process of acquiring backlinks to your website. [Jump to Search Engine Optimization (SEO)]
Local SEO :
Optimizing your website for local search results.
M
Marketing Automation :
Using software to automate repetitive marketing tasks.
Meta Description :
A brief summary of a web page consideration cycle.
Martech (Marketing Technology) :
Software and tools used to support marketing activities.
Mobile Marketing :
Marketing strategies that target mobile device users.
Multivariate Testing :
Testing multiple variations of a web page to see which performs best. [Jump to Conversion Rate Optimization (CRO)]
N
Natural Language Processing (NLP) :
A branch of artificial intelligence concerned with the interaction between computers and human language.
Negative Keywords :
Keywords you specifically tell search engines not to associate with your ads.
O
Off-Page SEO :
SEO activities that happen outside of your website, such as link building. [Jump to Search Engine Optimization (SEO)]
On-Page SEO :
SEO activities that happen on your website, such as keyword optimization and content creation.[Jump to Search Engine Optimization (SEO)].
Organic Search :
Search results that appear naturally on search engine results pages (SERPs) based on relevance, not advertising.
P
Paid Search :
Search engine marketing (SEM) where you pay to have your ads displayed on SERPs. Related article: Demystifying Paid Search: A Beginner’s Guide to SEM
Pay-per-click (PPC) :
Is a type of internet marketing which involves advertisers paying a fee each time one of their ads is clicked. Simply, you only pay for advertising if your ad is actually clicked on. See also Brand PPC
PECR :
PECR stands for Privacy and Electronic Communications Regulations. It’s a set of regulations in the UK that govern how organizations handle electronic communications data and privacy for individuals. Related Article: What is PECR compliance?
Pixel Tracking :
Placing a small piece of code on a website to track user behaviour.
Podcast :
An episodic series of spoken audio programs.
Programmatic Advertising :
Buying and selling advertising space using automated software.
Progressive Web App (PWA) :
A web application that offers app-like features without requiring an app download.
Q
Quality Score (Google Ads) :
A score assigned by Google Ads that reflects the relevance of your ad and keywords to user searches.
R
Real-Time Marketing :
Responding to current events and trends in your marketing messages.
Remarketing (Retargeting) :Targeting ads to users who have previously interacted with your website or brand. Related article: Spooky! The Ads are following you!
ROI (Return on Investment) :
The net profit of an investment.
RSS (Really Simple Syndication) :
A way to subscribe to updates from websites and blogs.
R.A.C.E. Framework
Developed by Smart Insights, the R.A.C.E. Framework is a customer journey-focused marketing strategy model. R.A.C.E. stands for:
Reach, Act, Convert, Engage. Related article: Mastering the Customer Journey: A guide to the R.A.C.E. Framework.
S
SaaS (Software as a service) :
SaaS Software as a service is a way of delivering applications over the Internet—as a service. Instead of installing and maintaining software, you simply access it via the Internet, freeing yourself from complex software and hardware management.
Schema Markup :
Adding data markup to your website to help search engines understand your content better.
Search Engine Marketing (SEM) :
Strategies for improving your website’s visibility in search engine results pages (SERPs).
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) :
The process of improving your website’s ranking in search engine results pages (SERPs).
Social Listening :
Monitoring online conversations to understand brand sentiment and customer needs.
Social Media Marketing (SMM) :
Using social media platforms to connect with your audience and promote your brand.
Stakeholder:
A stakeholder is an individual, group, or organization that has an interest in the success or failure of a company, project, or endeavor. Stakeholders can be impacted by the decisions or activities of the company or project, and they may also have the power to influence those decisions.
T
Technical SEO :
Optimizing the technical aspects of your website to improve crawling and indexing by search engines.
Top-Of-Mind Awareness (TOMA) :
A marketing strategy that aims to position your brand as the first one that comes to mind when a consumer thinks about a particular product or service category. It requires consistent and long-term marketing efforts.
U
User Experience (UX) :
The overall experience a user has when interacting with a website or app.
User Interface (UI) :
The visual design and layout of a website or app.
UTM Parameters :
Tags added to URLs to track the performance of marketing campaigns.
V
Voice Search :
Searching the internet using voice commands.
W
Website Analytics :
The process of collecting and analysing data about website traffic and user behaviour.
X
XML Sitemap :
A file that lists all the pages on your website to help search engines find and index them. [Jump to Search Engine Optimization (SEO)]
Y
YMYL (Your Money or Your Life) :
Websites that deal with topics that could potentially impact a user’s financial or physical well-being, such as health or finance. These websites are held to a higher standard by search engines.